Use only electrical equipment that is approved in the country you are working. However, use of approved equipment does not eliminate all dangers if the equipment is damaged or is used in adverse conditions, such as n rain or wet areas. Cord-connected portable equipment and supply cords must be maintained in good repair and be suitable for each condition of use. For example, the outer jacket of a cab-tire cord may appear undamaged but may conceal a broken ground conductor. Also, most electrical equipment manufacturers specify that their equipment should not be used in damp or wet conditions. Class A type ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) must be used for portable electrical equipment when working outside or in wet or damp conditions.
Safe work procedures
- Inspect tools, power cords, and electrical fittings for damage prior to each use. Repair or replace damaged equipment.
- Switch tools off before connecting to a power supply.
- Disconnect the power supply before making adjustments.
- Make sure tools are either properly grounded or double-insulated. Grounded tools must have a three-wire cord with a three-prong plug.This plug must be plugged into a properly grounded three-pole outlet.
- Do not break off the third (ground) prong on a plug.
- Test electrical tools and cords for effective grounding with a continuity tester before use.
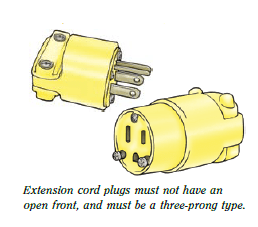
- Replace open-front plugs with dead-front plugs. Dead-front plugs are sealed and pose less danger of electric shock or short circuit (see diagram at right).
- Do not bypass the tool’s ON/OFF switch by connecting and disconnecting the power cord.
- Suspend power cords over walkways or working areas wherever possible to eliminate tripping hazards.
- Do not use extension cords as permanent wiring. They must only be used to temporarily supply power to an area that does not have a power outlet.
- Do not allow vehicles or equipment to pass over unprotected power cords. Cords should be put into electrical conduits or protected by placing them between two pieces of lumber of suitable strength.
- Keep power cords away from heat, water, and oil.
- Do not use light-duty power cords for heavy load applications.
- Do not carry electrical tools by the power cord.
- Do not disconnect the power supply by pulling or jerking the cord from the outlet. Pulling the cord rather than the plug may result in electric shock.
- Do not tie knots in power cords. Knots can cause short circuits and electric shocks. Loop the cords or use a twist lock plug.
- Do not clean tools with flammable solvents.
- Do not operate electrical tools in an area containing high levels of explosive vapours or gases.
- Do not overload the circuit by plugging several power cords into one outlet.